- Download and install the software.
- It will scan your computer for problems.
- The tool will then fix the issues that were found.
Windows Task Manager is one of those tools that most people don’t use very often. But it’s a pretty helpful tool that allows you to monitor processes, memory usage, CPU load, etc., on your system. This utility has been built into every version of Windows since Windows 95/98, and it’s still in Windows 10. However, some users are reporting seeing multiple instances of “Host Process for Windows TASKS,” or HPTT, running on their computers.
HPTT is a program that runs on all versions of Windows OS. It’s normal to see several instances of this process running, but what makes this unusual is that HPTT isn’t supposed to run unless you’re actively using Windows tasks. You shouldn’t even know about this process unless you open up Windows task manager and start looking around.
So why do we see multiple instances of this running on our systems? Well, it could just be a coincidence, but it might also be because someone installed something called “Task Scheduler.” If you’ve ever used Microsoft Office Outlook, you’ll probably recognize this software. You can set reminders, send emails, schedule appointments, etc. via this app. And if you install it, it will add itself to your startup programs list, making it easy to launch whenever you log onto your computer.
Table of Contents:
What does ‘host process for windows tasks’ mean?

Host Process for Windows Tasks serves as a host for Dynamic Link Libraries (DLL), which are used to load code into memory. These DLL files contain instructions that tell the operating system how to use certain functions within the application. For example, Microsoft Office programs use DLL files to access the functionality found in Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, OneNote, Access, Publisher, Visio, Project, FrontPage, InfoPath, SharePoint Designer, and many others. If one of those applications crashes, it could cause problems with another program, such as Internet Explorer, because the crash causes the DLL file to stop working.
To find out which services are hosting each taskhost.exe process listed in Task Manager, download Process Explorer and run it. Under the lower pane of the tool window, you’ll see a list of processes. A small icon represents each process, and clicking on it opens up the Properties dialog box. You can select the Name column header to sort the list alphabetically. Clicking on the name of a process displays information about it.
If you don’t know what a taskhost.exe process does, here’s a quick explanation. A taskhost.exe process is the main component of a task. Every executable program needs a taskhost.exe to start itself. The taskhost.exe process takes care of loading the necessary DLL files and starting the application.
What causes the ‘host process for windows tasks’ to show high CPU usage?
Over the years, we have regularly heard complaints about the Windows task host process taking up all your system resources. If you feel that your system is paralyzed, open the Windows Task Manager. In this window, you can see a list of running tasks, services, and other details – in multiple tabs. If you’ve done this, you’ve noticed a host process for Windows tasks.
The reason is simple: there are multiple entries with the same name that consume many resources at the same time. Some people think that multiple Host Processes for Windows Tasks are a virus. Others think it is a bug. But it’s not both. Before you try to stop a program or terminate a task, you should learn more about Host Processes for Windows Tasks.
How to repair the ‘host process for windows tasks’ high CPU usage?
Launch the SFC scanner
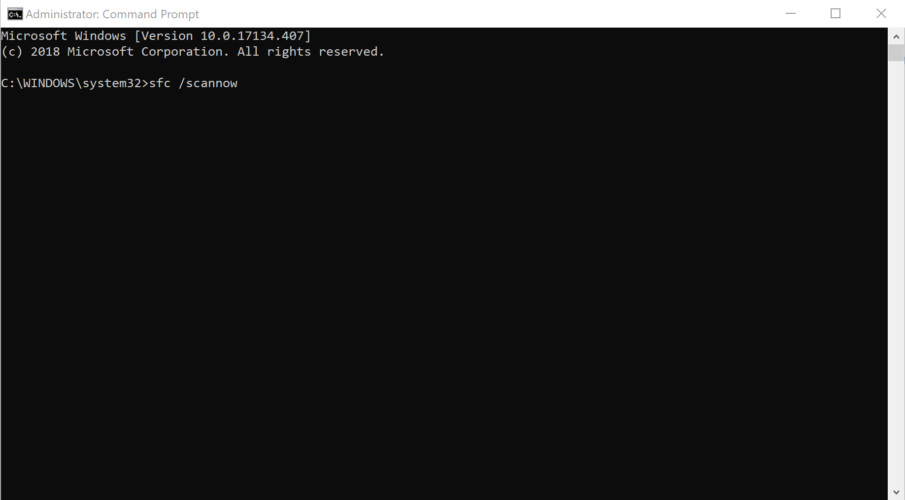
1. Press Windows+R keys to Open Run utility.
2. Type in cmd and press the CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER keys to Launch the Command Prompt with Administrative Privileges.
3. Type in “sfc /scannow”. You’ll see the system file checker screen pop up.
4. Click OK to continue. If you are prompted to reboot, do it now.
5. When the computer reboots, go ahead and log off. Once logged out, log back in again.
If there are no errors found, you’re done. Otherwise, follow these steps to fix the error(s).
Updated: June 2025
This tool is highly recommended to help you fix your error. Plus, this tool offers protection against file loss, malware, and hardware failures, and optimizes your device for maximum performance. If you already have a problem with your computer, this software can help you fix it and prevent other problems from recurring:
- Step 1 : Install the PC Repair and Optimizer Tool. (Windows 10, 8, 7, XP, Vista).
- Step 2 : Click Start Scan to determine what problems you are experiencing with your computer.
- Step 3 : Click Repair Allto resolve all problems.
Start the DISM command
1. Type the following two commands into your Command Prompt:
Dism /online /cleanupimage /startcomponentcleanup
Dism /online/cleanupimage/restorehealth
2. Press Windows + R keys on your keyboard. You’ll see a prompt asking you to confirm whether you want to restart Windows. Click Yes.
3 . You’ll now see a progress bar indicating how long it will take to complete the process.
4. When the process completes, you’ll see a message saying, “Windows completed the requested action.”
If you’re having trouble seeing the above steps, you can watch our video tutorial here.
Use the memory diagnostics tool in windows
This tool will help identify any memory errors or other hardware issues that could cause your computer to slow down or crash. You don’t need to reboot your system; simply run the Windows Memory Diagnostic Test and let the tool do its job. If there are any problems found, you can use one of the following methods to resolve them:
1. Repair Your Computer
2. Reinstall Your Operating System
3. Update Drivers
4. Reset Your PC Settings
5. Restore Default Settings
6. Delete Unwanted Files
Identify and repair corrupted BITS files
If you are experiencing problems downloading BitTorrent files, it could be because your computer has been infected with malware. Malware programs often use file sharing protocols like BitTorrent to spread themselves throughout your system. To fix this problem, follow the steps below.
1. Restart your PC.
2. Log into your account.
3. Locate the “BITS” folder under Local Disk (C)—Right-click on it and select Properties.
4. Click on General Tab.
5. Select the option labeled Hidden Files and Folders.
Make sure your computer is malware-free by scanning it
Malicious software, known as malware, can do anything from slow down your computer to spying on what you’re doing online. You might think it’s impossible to catch viruses, spyware, and adware, but there are ways to protect yourself against malicious software.
There are many different kinds of malicious software, so make sure you know how to identify each one. For example, some types of malware are designed to steal personal information like credit card numbers, while others can slow down your computer or even crash it.
You can use several methods to scan for malware. You can scan your computer with an antivirus program because it’s quick and easy. If you don’t already have an anti-malware program installed, download one now.
Once you’ve scanned your computer, you’ll want to clean out any leftover items. Here’s how to do that:
1. Open Control Panel.
2. Click Uninstall a Program.
3. Locate the program you want to uninstall.
The system should be restarted
Restarting the system may help you reduce high Disk Usage for the host process for Windows. If the problem persists, it could indicate a severe issue such as malware infection or hardware failure. You must restart the computer to fix these problems. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Click Start, type cmd into the Search box, and press ENTER.
2. In the Command Prompt window, enter ipconfig /flushdns followed by pressing ENTER. This command resets DNS settings.
3. Press CTRL + ALT + DEL keys together to open Task Manager.
4. Select the Services tab.
5. Scroll down to find the name of the host process for Windows listed under the Service Status column.
6. Right-click the selected service and select Stop.
Install the latest Windows update
Microsoft releases regular security updates to protect against viruses and malware. These are called “security patches.” They fix bugs in software programs. Sometimes Microsoft sends out multiple updates per month. You can download the latest version of Windows 10 directly from Microsoft’s website.
If you’re running Windows 7 or 8, you can’t use the automatic updating feature. Instead, you’ll need to check for updates manually. Here’s what to do:
1. Click the ‘ windows updates.’
2. Wait until all available updates are downloaded.
3. Install them.
4. Reboot your computer.
Restart Windows with a clean boot
A clean boot helps determine whether a background process is causing system instability. If it turns out that there are issues with a particular application, you can disable it without affecting the rest of the operating system.
This method works best if you use Windows 10 Home edition because it includes a built-in tool called System Configuration Utility that lets you perform a clean boot. Selective Startup allows you to activate some programs and deactivate others. When you select one item, all the other applications remain inactive.
In addition, you can choose to keep running processes enabled or disabled. To do this, open Task Manager and click More Details. Then, under the Processes tab, click the small arrow next to each program listed and select Enabled or Disabled.
APPROVED: To fix Windows errors, click here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if you stop the Host Process for Windows Tasks?
You should not remove, disable or stop Host Process for Windows Tasks on your computer. Host Process for Windows Tasks plays an essential role in loading DLL-based services on your system. Disabling the Host Process for Windows Tasks can cause your system to crash.
Is Host Process for Windows Tasks necessary?
Host Process for Windows tasks is necessary for most system services to load correctly and is an important component in all versions of Windows. These services are necessary for the operating system to work correctly.
Why does my computer show 100% hard disk usage?
If your hard drive is 100% used in Windows 10, the problem may be caused by Windows itself or a variety of other programs. There can be many reasons, from Windows Superfetch to a virus or malware, outdated drivers, or firmware. Often your problem is the result of more than one cause.

